Editor’s Note: StrategicCIO360’s parent company, Chief Executive Group, has put together an afternoon of learning and strategizing to help you understand this critical technology: The C-Suite’s Guide to Generative AI: Practical Applications and Uses, June 26. Join us, online 2-5 pm >>
AI carries great potential for business—and science—but it also comes with risk. There’s been mounting discussions from governments and experts around the world about the technology’s safety and the need for regulation.
But none of that appears to be stopping public companies from adopting the technology—not even board members saying they do not feel as well informed as they should be to provide oversight on the matter.
Nearly half (44 percent) of the 140 U.S. public company directors participating in our May Director Confidence Index—a monthly poll of director sentiment in business conditions conducted by Corporate Board Member and Diligent Institute—said their companies were already using AI in some capacity, and another 32 percent said that they were working to do so in the short term. Only 6 percent said they had no plans to use AI whatsoever—at least for now—and 14 percent said they didn’t know if their company was using or planning to use AI.
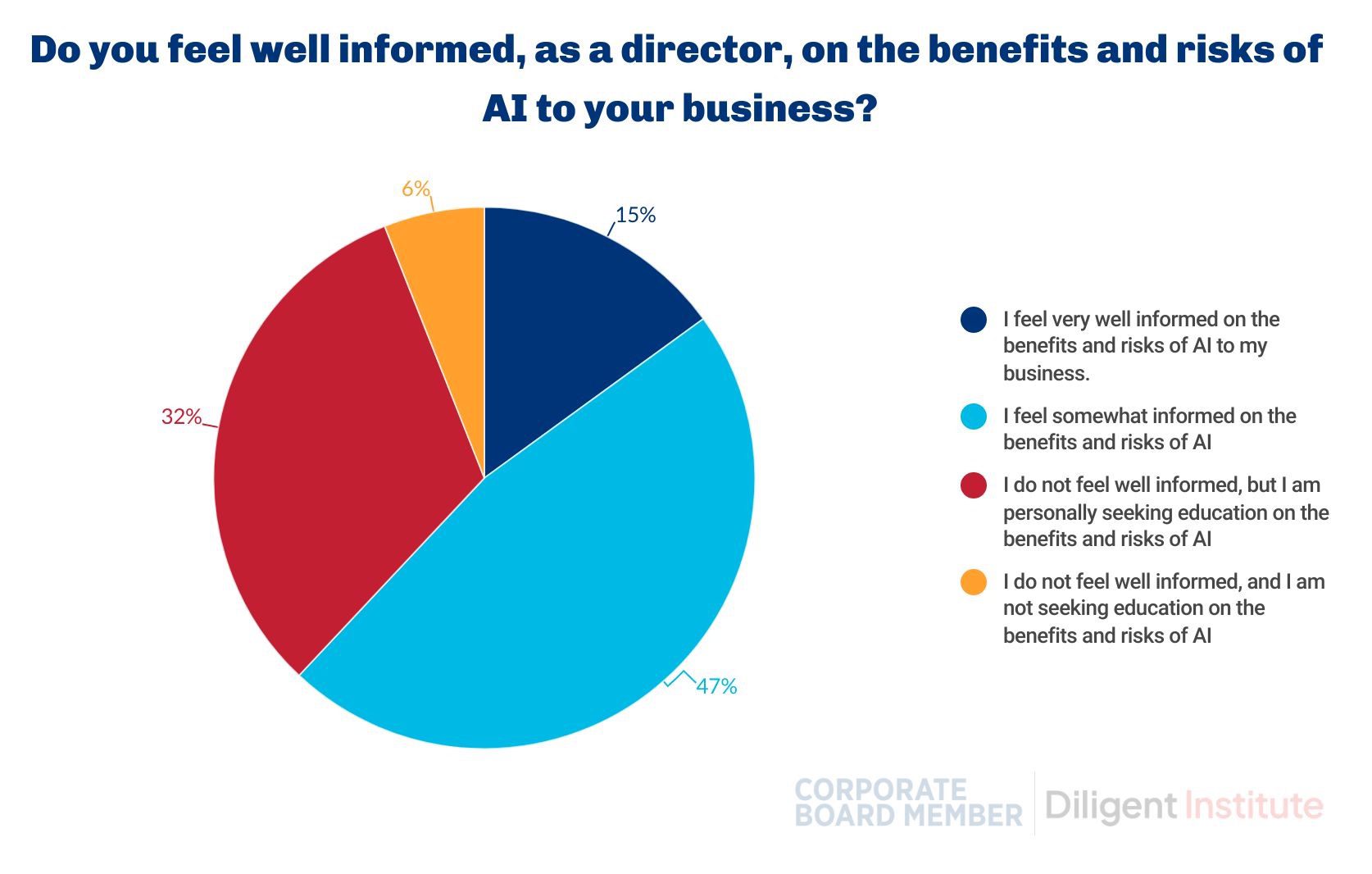
Yet, only 15 percent of the directors participating in the survey said they felt well informed about the benefits and risks of using AI.
Data from Diligent Institute’s Corporate Sentiment Tracker, an AI-powered tool monitoring what topics corporate leaders are speaking about the most frequently in the news, shows “AI” as the number one most spoken about single term of the past 90 days, and “Emerging Technology Risk” as a top topic being discussed in the same time period.
Our survey data confirms this: Half of the directors polled said their board was increasingly discussing the issue, and 31 percent said the use of AI had driven them to also independently seek education on the matter.
Others, however, felt it was still too early in the AI cycle to focus board time on the matter, and that as AI’s influence, use and liability evolves, “board education will move along with to ensure appropriate use and application,” said one respondent.
“Directors have a lot on their plate,” said Dottie Schindlinger, executive director of the Diligent Institute and a partner in this research, “And many of them might see AI as just one more area of risk they have to tackle—and they might not feel well-versed enough in technology risk in general to feel competent providing adequate oversight. But considering the far-reaching implications of the technology, directors would be well advised to get up-to-speed fast and not ignore what is likely to be the most disruptive technology of our lifetimes.”
Directors are in a unique position to help their companies mitigate the risks of new technologies by asking management teams smart questions. We recently published a great conversation between CBM’s editor in chief, Dan Bigman, and Tom Davenport, a professor at Babson University and the author of All In on AI, in which Davenport offers a fascinating framework for directors looking to process and harness all this change and successfully evaluate its use. You can read it here.
Diligent Institute has also been working fast to respond to the uptick in pressure on directors to get better informed on AI and other sources of cyber risk and opportunity through the Cyber Risk & Strategy Certification. The program explores emerging tech along with other cyber risk oversight issues that directors are feeling pressured to embrace.
How Companies Are Using AI
Among those directors who said their companies are already using AI, 47 percent said they did so in customer-facing operations, and 23 percent said for external content generation.
“This aligns to what we’ve been hearing anecdotally—companies have long been adopting technology like chatbots for customer-facing operations,” says Schindlinger. “And solutions like ChatGPT are a very natural fit for content generation—that is, as long as teams responsible do a careful job of supervising and vetting AI-generated content. The key is understanding and mastering emerging technology—and using it to your advantage.”
A deeper look into the data finds different sectors utilizing AI in different ways. For instance, companies in the IT and Consumer Discretionary sectors are making use of the technology primarily in their customer-facing operations (50 and 43 percent, respectively), while Energy directors primarily responded that their use of AI revolved around administrative and finance tasks (44 percent).
As for external content generation, we found a greater number of Healthcare directors selecting that option (20 percent) than in any other sector—though the most common use of AI in that sector remains customer-facing operations (35 percent).
AI Use Cases in the Boardroom
If a good proportion of companies are already tapping into AI’s capabilities, fewer are seeing the value of the technology in the governance process. Thirty-seven percent of directors said AI can be used to support directors in making faster, more informed decisions, but the same proportion said that while AI can have a seat at the table, the boardroom should/will always be led by humans.
More than a quarter (26 percent) said they see no role for AI in corporate governance at all.
When asked how AI can best benefit the board specifically, 75 percent said at the audit committee level. How, however, remains to be discussed. AI-powered audit processes can be a game-changer for boards, but they would also be a big liability if not properly checked by humans.